Dive into the world of loan amortization schedule, where numbers dance and financial planning takes center stage. Brace yourself for a journey through the intricacies of loan repayment, as we unravel the complexities in a way that’s both informative and entertaining.
Whether you’re a financial guru or just starting to dip your toes into the world of loans, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of loan amortization schedules.
What is a loan amortization schedule?
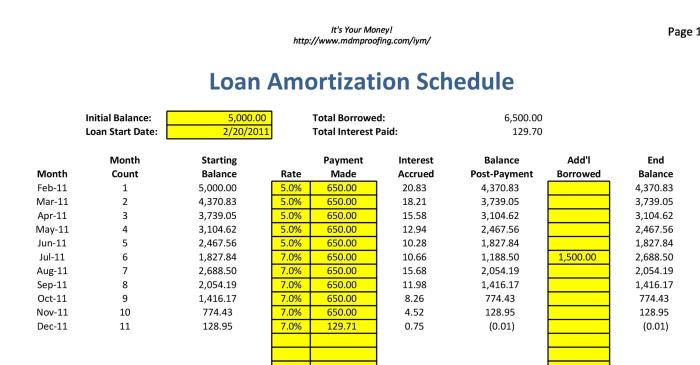
A loan amortization schedule is a table that shows the breakdown of each periodic loan payment. It Artikels how much of each payment goes towards the principal amount of the loan and how much goes towards interest.
When you take out a loan, such as a mortgage or car loan, the lender provides you with a payment schedule. This schedule includes the total amount you owe, the interest rate, and the term of the loan. The loan amortization schedule breaks down each payment over the life of the loan, showing you how much of each payment goes towards reducing the principal balance and how much goes towards paying off the interest.
Types of Loan Amortization Schedules
- Fixed-Rate Mortgage: For example, a 30-year mortgage where the interest rate remains the same throughout the term of the loan.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgage: In this type of loan, the interest rate can change periodically, affecting the amount of each payment that goes towards interest and principal.
- Car Loan: A loan taken out to finance the purchase of a vehicle, with a specific term and interest rate.
Components of a loan amortization schedule
When looking at a loan amortization schedule, there are several key components that play a crucial role in understanding how the loan will be paid off over time.
Loan Amount
The initial loan amount is the total sum borrowed from the lender. This amount is the starting point for calculating the amortization schedule and determines the total repayment amount.
Interest Rate
The interest rate is the percentage charged by the lender for borrowing the money. It is a crucial component as it determines the amount of interest paid each period and impacts the total cost of the loan.
Loan Term
The loan term is the length of time over which the loan will be repaid. It is usually expressed in months or years. The loan term affects the monthly payment amount and the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Monthly Payment
The monthly payment is the fixed amount paid each month towards the loan. It consists of both principal and interest portions. Understanding the monthly payment helps borrowers budget and plan for the repayment.
Principal Payment
The principal payment is the portion of the monthly payment that goes towards reducing the loan balance. As the loan is paid down, the portion of the payment allocated to principal increases, while the interest portion decreases.
Interest Payment
The interest payment is the portion of the monthly payment that goes towards paying the interest charges on the loan. In the early stages of the loan, a larger portion of the payment goes towards interest, gradually decreasing over time as the principal balance reduces.
Outstanding Balance
The outstanding balance is the remaining amount owed on the loan after each payment is made. It decreases with each payment as the principal is paid down. Tracking the outstanding balance helps borrowers see how much is left to pay off.
Amortization Schedule
The amortization schedule is a table that shows a detailed breakdown of each payment over the life of the loan. It includes the payment number, payment amount, interest paid, principal paid, and the remaining balance for each period.
Calculating loan amortization.
When it comes to calculating loan amortization, it involves breaking down your loan payments into equal installments that cover both the principal amount and the interest accrued over time. This process helps you understand how much of each payment goes towards reducing the principal balance and how much goes towards paying off the interest.
Manual Calculation Process
To calculate loan amortization manually, you can use the following formula:
Monthly Payment = P * r * (1 + r)^n / ((1 + r)^n – 1)
Where:
– P is the principal loan amount
– r is the monthly interest rate (annual interest rate divided by 12)
– n is the total number of payments (loan term in months)
You can then calculate the remaining loan balance after each payment by subtracting the principal portion of the payment from the previous balance and adding the interest accrued for that period.
Comparison with Automated Tools
Automated tools or software can simplify the process of calculating loan amortization by providing accurate results quickly. These tools use algorithms to calculate the monthly payments, interest, and principal portions, as well as the remaining balance after each payment. They eliminate the need for manual calculations and reduce the risk of errors.
Formulas Used
- The formula for calculating the monthly payment was mentioned earlier:
- To calculate the interest portion of each payment:
- To calculate the principal portion of each payment:
- To calculate the remaining balance after each payment:
Monthly Payment = P * r * (1 + r)^n / ((1 + r)^n – 1)
Interest Payment = Previous Balance * r
Principal Payment = Monthly Payment – Interest Payment
New Balance = Previous Balance – Principal Payment
Importance of a loan amortization schedule.
Having a loan amortization schedule is crucial for borrowers as it provides a clear breakdown of their repayment plan over time, helping them stay on track with their financial obligations.
Benefits for Borrowers
- Allows borrowers to see how much of each payment goes towards principal and interest, helping them understand the cost breakdown.
- Enables borrowers to plan their budgets effectively by knowing the exact amount due each month, helping avoid missed payments.
- Assists borrowers in making informed decisions about refinancing or paying off the loan early by providing a clear picture of the remaining balance.
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Loan amortization schedules play a crucial role in financial planning and budgeting by providing borrowers with a structured repayment plan. This allows them to allocate funds efficiently and ensure they can meet their payment obligations without financial strain.
Risk Management for Lenders
- Lenders use loan amortization schedules to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and evaluate their ability to repay the loan.
- Helps lenders manage risks by providing a detailed repayment timeline, allowing them to anticipate potential payment defaults and take timely actions to mitigate risks.