Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of Behavioral biases in investing! From irrational decisions to psychological influences, we’re about to unravel the mysteries behind investor behavior in a way that’ll keep you hooked until the very end.
As we delve deeper into the various types of biases and their impact on investment choices, you’ll gain a whole new perspective on how our minds can sometimes lead us astray in the financial realm.
Overview of Behavioral Biases in Investing
Behavioral biases in investing refer to the psychological tendencies or cognitive errors that can influence investment decisions. These biases can lead investors to make irrational choices based on emotions rather than facts or logic.
Impact of Behavioral Biases on Investment Decisions
- Overconfidence Bias: Investors may believe they have superior knowledge or skills, leading them to take on too much risk.
- Loss Aversion Bias: Investors feel the pain of losses more than the pleasure of gains, causing them to sell investments prematurely.
- Confirmation Bias: Investors seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs, ignoring contradictory data.
Examples of Common Behavioral Biases
- Herding Bias: Following the crowd without conducting independent research.
- Anchoring Bias: Fixating on a specific price or value, even when new information suggests otherwise.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Making investment decisions based on the fear of missing out on potential gains.
How Behavioral Biases Lead to Irrational Choices
Investors may succumb to these biases by letting emotions drive their decisions, rather than relying on objective analysis and research. This can result in buying high during market euphoria and selling low during panics, ultimately leading to poor investment performance.
Types of Behavioral Biases
When it comes to investing, behavioral biases can greatly impact decision-making. These biases are systematic errors in thinking that can affect individuals’ choices, often leading to suboptimal outcomes in the world of finance. Let’s explore some common types of behavioral biases in investing and how they can influence investment behavior.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one’s preexisting beliefs or hypotheses. In investing, individuals may only seek out information that supports their investment thesis while ignoring contradictory evidence. For example, an investor who is bullish on a particular stock may only pay attention to positive news about the company while disregarding any negative signals. This bias can lead to overconfidence in one’s investment decisions and a failure to consider all relevant information.
Overconfidence
Overconfidence bias occurs when individuals overestimate their abilities or knowledge, leading them to take on more risk than they should. In investing, this bias can manifest as investors believing they have an edge over the market and making overly aggressive trades. For instance, a trader may consistently believe they can outperform the market and take on excessive leverage, leading to significant losses. Overconfidence can cloud judgment and lead to poor decision-making in the financial markets.
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is the tendency for individuals to strongly prefer avoiding losses over acquiring gains. In investing, this bias can cause investors to hold on to losing investments for too long, hoping that the situation will improve. For example, an investor may refuse to sell a stock that is plummeting in value because they are afraid of realizing a loss. This reluctance to accept losses can lead to missed opportunities and a failure to rebalance a portfolio effectively.
Overall, understanding these behavioral biases is crucial for investors to make more rational and informed decisions in the financial markets. By recognizing and mitigating these biases, individuals can strive to improve their investment outcomes and achieve long-term success.
Psychological Factors Influencing Investment Decisions
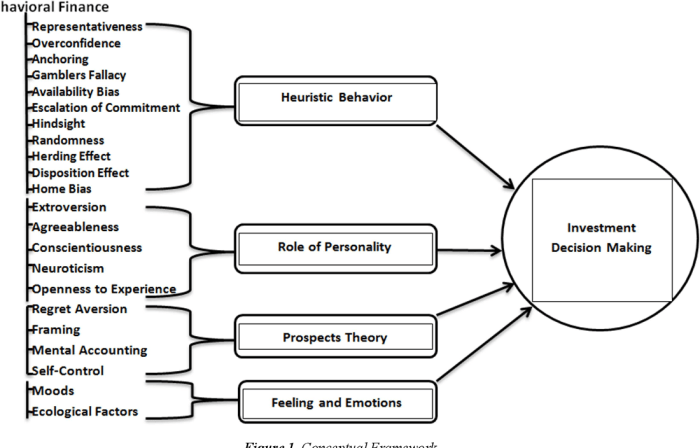
Emotions, beliefs, and past experiences play a significant role in shaping investment decisions. These psychological factors can lead to biases that impact how investors perceive and act in the financial markets. Let’s delve into how these factors influence investment choices and the cognitive processes involved.
Emotions in Investment Decisions
Emotions such as fear, greed, and overconfidence can cloud judgment and lead to irrational investment decisions. For example, fear of missing out (FOMO) may drive investors to make impulsive decisions, while overconfidence can result in excessive risk-taking without proper evaluation of the potential consequences.
Beliefs and Cognitive Processes
Beliefs about the market, specific investments, or economic conditions can influence how investors interpret information and make decisions. Confirmation bias, where investors seek out information that aligns with their existing beliefs, can lead to ignoring contradictory evidence and making biased decisions. Cognitive processes such as heuristics and mental shortcuts also impact how investors process information and make judgments.
Social Influence on Investor Behavior
Social influence, including peer pressure, media influence, and herd mentality, can shape investor behavior. Investors may feel compelled to follow the crowd or make decisions based on social cues rather than independent analysis. This can lead to herd behavior, where investors collectively move in the same direction without considering the underlying fundamentals of an investment.
Mitigating Behavioral Biases in Investing
Investing can be heavily influenced by behavioral biases, leading to irrational decision-making. To counteract these biases, investors can employ various strategies to make more informed choices and reduce the impact of emotions on their investments. Recognizing these biases and understanding how they affect decision-making is crucial in mitigating their negative effects.
Strategies to Counteract Behavioral Biases
- Implementing a rules-based approach: Creating a set of investment rules and sticking to them can help investors avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions.
- Seeking diverse opinions: Consulting with financial advisors or other investors can provide different perspectives and help counteract confirmation bias.
- Utilizing technology: Using automated investment tools and algorithms can help remove emotional biases from decision-making processes.
Tips for Investors to Overcome Biases
- Practice mindfulness: Being aware of your emotions and biases can help you make more rational investment decisions.
- Take a long-term view: Focusing on the long-term goals of your investments can help reduce the impact of short-term market fluctuations.
- Continuously educate yourself: Stay informed about behavioral finance concepts and regularly review your investment strategies to identify and address biases.
Importance of Education and Awareness
- Education is key: Understanding behavioral biases and how they influence decision-making is essential for investors to navigate the complexities of the market.
- Awareness leads to better decisions: By recognizing when biases are at play, investors can take steps to counteract them and make more rational choices.
- Continuous learning is crucial: Staying informed about new research and developments in behavioral finance can help investors continually improve their decision-making processes.