Diving deep into the world of Asset allocation strategies, this intro sets the stage for a mind-blowing exploration of investment tactics that will have you feeling like the coolest investor on the block. Get ready to learn how to rock your investment portfolio like a pro!
In this article, we’ll break down the different types of asset classes, traditional models, and modern theories that will help you navigate the complex world of asset allocation with style and finesse.
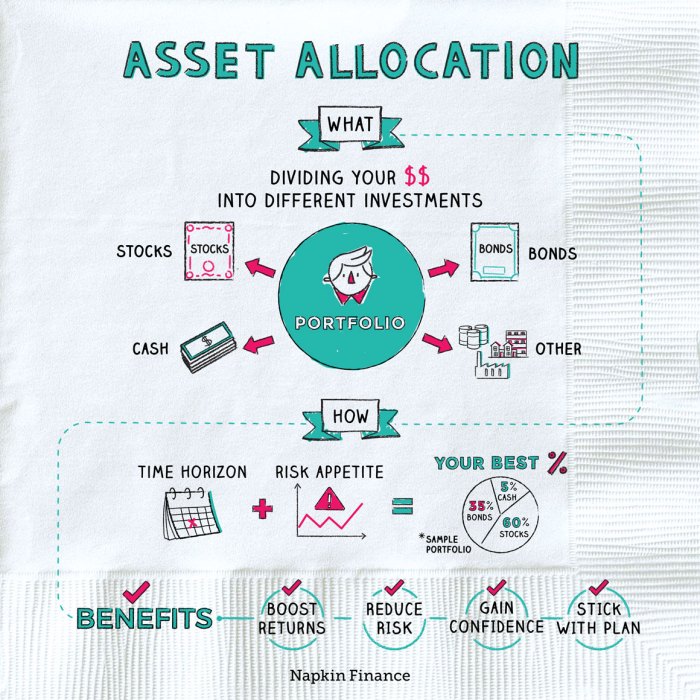
Overview of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies refer to the process of spreading and diversifying investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents, to manage risk and optimize returns.
Asset allocation is crucial in investment portfolios as it helps investors achieve a balance between risk and return based on their financial goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. By allocating assets strategically, investors can minimize the impact of market volatility and potentially enhance long-term performance.
Importance of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation plays a vital role in determining the overall risk and return profile of an investment portfolio. By diversifying across various asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market fluctuations on their portfolios. This can help mitigate potential losses during market downturns and provide more consistent returns over time.
- Asset allocation helps investors achieve a desired level of risk exposure based on their individual financial objectives.
- By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can capture the potential upside of different market segments while reducing overall portfolio risk.
- Proper asset allocation can lead to a more stable and resilient portfolio, especially during turbulent market conditions.
Benefits of Diversification through Asset Allocation
Diversification through asset allocation involves spreading investments across a range of asset classes, industries, and regions to minimize concentration risk and enhance portfolio resilience.
- Diversification helps reduce the impact of adverse events on a single asset or sector, thereby lowering overall portfolio risk.
- By combining assets with low or negative correlations, investors can potentially achieve smoother returns and improved risk-adjusted performance.
- Asset allocation diversification can provide opportunities for capital growth and income generation across various market environments.
Types of Asset Classes for Allocation
When it comes to asset allocation, there are several types of asset classes that investors commonly consider. Each asset class has its own characteristics, risks, and behaviors in varying market conditions.
Stocks
- Stocks represent ownership in a company and are considered equity investments.
- They offer the potential for high returns, but also come with high volatility and risk.
- Stocks tend to perform well during periods of economic growth but can experience significant losses during market downturns.
Bonds
- Bonds are debt investments where investors lend money to a corporation or government in exchange for periodic interest payments.
- They are generally considered less risky than stocks but offer lower potential returns.
- Bonds are more stable and can provide income and capital preservation, especially during market downturns.
Real Estate
- Real estate includes properties like residential homes, commercial buildings, and land.
- Investing in real estate can provide rental income and potential appreciation in property value.
- Real estate investments have the potential for both income generation and capital appreciation but can be illiquid and subject to market fluctuations.
Commodities
- Commodities include natural resources like gold, oil, and agricultural products.
- Investing in commodities can provide diversification and a hedge against inflation.
- Commodities tend to perform differently from traditional asset classes like stocks and bonds and can be influenced by factors like supply and demand dynamics.
Traditional Asset Allocation Models
When it comes to traditional asset allocation models, one of the most popular strategies is the 60/40 portfolio. This model typically involves investing 60% of the portfolio in equities and 40% in fixed income securities.
The principle behind the 60/40 portfolio is to strike a balance between risk and return. Equities tend to offer higher potential returns but come with higher volatility, while fixed income securities provide stability and income but with lower returns. By combining the two asset classes in a 60/40 ratio, investors aim to achieve a diversified portfolio that can weather market fluctuations while still capturing growth opportunities.
Comparison of Traditional Models
- The 70/30 portfolio: This model allocates 70% to equities and 30% to fixed income, offering a higher risk and return profile compared to the 60/40 portfolio. It may be more suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance and longer investment horizon.
- The 50/50 portfolio: With an equal split between equities and fixed income, the 50/50 model aims to provide a balanced approach to risk and return. It may be suitable for investors with a moderate risk tolerance seeking a more conservative strategy.
- The 80/20 portfolio: This model allocates 80% to equities and 20% to fixed income, emphasizing growth potential over stability. It is considered a more aggressive strategy and may be suitable for investors with a high risk tolerance and long-term investment goals.
Modern Portfolio Theory and Asset Allocation
Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) is a framework developed by Harry Markowitz that focuses on maximizing returns while minimizing risk through diversification. It plays a crucial role in asset allocation by providing a systematic approach to building investment portfolios.
Optimizing Asset Allocation with MPT
Modern Portfolio Theory helps in optimizing asset allocation by considering the correlation between different asset classes. By diversifying investments across assets with low correlation, MPT aims to reduce overall portfolio risk without sacrificing returns.
- Allocating a portion of the portfolio to assets with negative or low correlation can help offset losses in one asset class with gains in another.
- By analyzing historical data and risk metrics, MPT enables investors to construct portfolios that offer the best possible risk-return trade-off for their investment goals.
Examples of Applying MPT in Portfolio Construction
Let’s look at how Modern Portfolio Theory can be applied in constructing diversified investment portfolios:
| Asset Class | Expected Return | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks | 8% | 15% |
| Bonds | 4% | 5% |
| Real Estate | 6% | 10% |
By combining stocks, bonds, and real estate in a diversified portfolio based on MPT principles, investors can achieve a balance between risk and return that aligns with their risk tolerance and investment objectives.